The quotes property in CSS allows you to specify which types of quotes are used when quotes are added via the content: open-quote; or content: close-quote; rules. Here’s how to use it:
q {
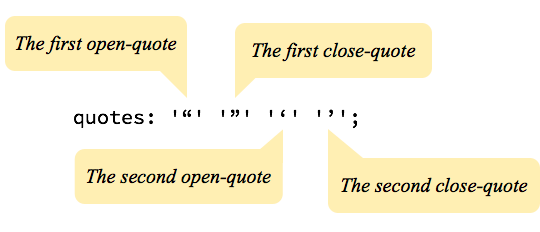
quotes: "“" "”" "‘" "’";
}
q::before {
content: open-quote;
}
q::after {
content: close-quote;
}In the example above, four values are added. A set of double smart quotes and a pair of single smart quotes. It’s slightly confusing as each quote is wrapped in quotes – but those are just programmatic quotes (could be double (“) or single (‘)) as anywhere else in CSS. The quotes inside are what will be used on the page.
There are four values for the content property that relate to the quotes property: open-quote, close-quote, no-open-quote, and no-close-quote.
The first pair of quotes in the value are the opening and closing quotes. The second pair are the opening and closing quotes for quotes nested one level deep within other quotes that also use the quotes property. E.g. a <q> element inside of a <q> element.
A few examples:
Double quotes on the first quote,
single quotes on the second.
A quote with French quotes.
You can place as many pairs of quotes in the quotes property as you like. But you don’t have to put more than two, because for every extra quote it simply repeats the quotes values from the beginning.
The no-open-quote and no-close-quote values stop the quotes from displaying, but they continue to increment the quote depth.
More Information
- Don’t use the
<q>element unless you’re quoting someone. In all other cases (irony, sarcasm, or whatever else you use quotes for) simply use the quotation marks themselves (like these: “ ”). - This isn’t just for the
<q>element, it could be<blockquote>too or anything else. - Quotes & Accents
Related Properties
Other Resources
Browser Support
| Chrome | Safari | Firefox | Opera | IE | Android | iOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11+ | Any | 1.5+ | 4+ | 8+ | Any | Any |

Not my quote, but I have adopted it.
“Great design will make people love your product/company”
gracias desde peru :D!
In multilingual sites we can use
langattribute onhtmltag, instead of adding class to quote. Like this:After a lot of research, including looking at a lot of online versions of newspapers for usage and consistency, I found that while the official style guides for countries may specify the quote characters, there is such a wide variation in usage within a country that trying to tie the quote characters to the language for general purpose use might create frustrations.
For example, in France, the guillemots seem to only be used in traditional newspapers, but most across the rest of the country were going with inward-facing or plain double quotes, as in the US. Same with Spain. And it is like that almost everywhere else, except North Korea!
It seems to be a further example of the web’s influence on national cultures, with online writers probably more influenced by the prodigious US online presence, than their own print media. I know some would like ‘proper’ style to be used within their nations, but such things are a lot more fluid these days, because what is ‘normal’ comes with a larger deviation range than it used to!
It is coming down to knowing what one’s readers are used to. If they don’t expect guillemots, providing them may give the wrong impression of how ‘hip’ one is.
For the tools I am creating, I will be offering the main 19 variations of two-level quote character combinations for selection along with the language.
Unfortunately, I just found out that Chrome does not like using quotes specified using the css quotes attribute, so I will have to see if there is a workaround.
At least the html dir=rtl attribute can be derived from languages starting with ‘ar’, ‘dv’, ‘fa’, ‘he’, ‘ps’, ‘ur’ or ‘yi’. Unfortunately, that has to be via a php function, and not css. :(
In most cases you’re better off using the
:lang()pseudoclass, cf. http://www.w3.org/International/questions/qa-css-langWhich quotation mark should be rendered on a multilingual page does not depend on the language of the whole page, but on the language of the text surrounding the quote, cf. https://lists.w3.org/Archives/Public/www-international/2011JulSep/0069.html Use
:lang(fr) > q.In French typography there are spaces between the quote and the quotation marks, i.e.
quotes: "«\A0" "\A0 »";@ Patanjali
Yeah, that’s because guillemets are not easily reachable on a keyboard. And the funny story is that the previous french gov actually missioned a standards’ org to design a keyboard layout on which they would (as well as accentuated characters).
The most infuriating thing is definitely the spec, which is plain wrong for french defaults.
It suggests “«” “»” “«” “»” as a default but it is just wrong.
First, you need a non-breaking (thin) space after the opening quote and before the closing quote. Then, nested quotes should be curly quotes because having nested guillemets makes a text unreadable.
French readers have no issue at all with guillemets. They get used to it as soon as they start reading (it is used everywhere except on John Doe’s computer because it takes an insane Windows alt-d+ combo to access guillemets).
As a matter of fact, straight quotes are considered amateurish, typographically wrong and, more importantly, disrespectful of the french language/culture in some contexts.
Found I needed to backslash escape those double quotes in the ‘quotes’ property to get them working.
Using Chrome 28.0.1500.71 on Mac OS X.
That is because you are (incorrectly) using straight quotes instead of typographic quotes (see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quotation_mark).
I had come across a site that has an online css compressor that converted a sequence like “{quotes:’\201C’ ‘\201D’ ‘\2018’ ‘\2019’;}” to “{quotes:201C201D20182019;}”, though I left it at “{quotes:201C 201D 2018 2019;}” for readability. It worked across most browsers, except desktop and mobile Chrome.
After reading your post, I changed it back, and have got Chrome working again!
THANK YOU!
With Chrome, it is not all that simple.
With other browsers (IE, Samsung, iOS), applying a style defining the quotes on the body and descendent elements produces the expected results, namely:
a) The body element definition rules, unless a descendant element also has one, irrespective of lang attribute.
b) If a q element has a style for quotes, only an embedded q element gets the new style, while the parent still has it antecedent quotes, irrespective of lang attributes on any of the elements.
Unfortunately, Chrome only obeys the styles IF there are no lang attributes on an element. As soon as the lang attribute is applied to an element, the quotes ‘officially’ applicable to the lang attribute apply to its descendent q elements, BUT also to it, if it is a q. That totally screws it all up.
It would be fine if:
a) All browsers did it.
b) Everybody used the ‘official’ quotes for a language.
c) Chrome applied it to the body element.
The lang attribute is used semantically, perhaps for language tools (spelling, grammar), as it is not actually required for laying out text in the required direction, but the appropriate dir attribute, which can be directly derived from lang (by using a custom php function), IS required to ensure the appropriate alignment of other elements, like tables and fieldsets.
Now, I am designing tools for HTML dummies, and want to avoid having users lumped with having to deal with such issues. I expect that most will not be doing multiple languages on the same page, but I would like things to applied in an ‘orthogonal’ (consistent and regular) way, in that specifying the language for a semantic element, like a section, will make its content lay out appropriately, but that they can choose the quote set appropriate to their target audience.
With this Chrome issue, it appears that I have to choose one of:
a) Let Chrome users live with it. That is, suffer possibly odd quotes on q elements with a lang attribute, or within language-specific blocks.
b) Make page writers (the ‘dummies’) specify the dir attribute explicitly, but leave off the lang attribute.
c) Make page writers put in explicit quotes everywhere.
I am tempted towards a) because for:
a) Only surfaces if requiring embedded quotes within another language. I am not expecting my users to be sophisticated users of multiple languages in the one page. Of course, they would have to NOT use a quote class on a first level q element, though that is not semantically correct.
b) I would prefer direction to be explicitly tied to language use, which is the
principal reason to be using it in the first place. My target users would be very unlikely to use it for any other reason.
c) I want to avoid users having to make too many micro-decisions.
Any comments?
Actually, defining my quotes in css properly made them independent of the lang attribute, though it does mean that one of the classes MUST be used on EVERY element where a lang attribute is used.
My styles (use as you wish) are:
/QUOTES/
body{quotes:'\201C' '\201D' '\2018' '\2019';}/“”‘’DEFAULT/
.Q_SuiDui * {quotes:'\2018' '\2019' '\201C' '\201D';}/‘’“”/
.Q_DuiSui * {quotes:'\201C' '\201D' '\2018' '\2019';}/“”‘’/
.Q_DS * {quotes:'\22' '\22' '\27' '\27';}/""''/
.Q_DsS * {quotes:'\301D' '\301E' '\27' '\27';}/〝〞''/
.Q_GdoGso * {quotes:'\AB' '\BB' '\2039' '\203A';}/«»‹›/
.Q_GdoDui * {quotes:'\AB' '\BB' '\201C' '\201D';}/«»“”/
.Q_GdoDol * {quotes:'\AB' '\BB' '\201E' '\201D';}/«»„”/
.Q_NK * {quotes:'\300A' '\300B' '\3008' '\3009';}/《》〈〉/
.Q_CJK * {quotes:'\300C' '\300D' '\300E' '\300F';}/「」『』/
.Q_DooSoo * {quotes:'\201E' '\201C' '\201A' '\2018';}/„“‚‘/
.Q_DolSui * {quotes:'\201E' '\201D' '\2018' '\2019';}/„”‘’/
.Q_DolSul * {quotes:'\201E' '\201D' '\2019' '\2019';}/„”’’/
.Q_DolGdo * {quotes:'\201E' '\201D' '\AB' '\BB';}/„”«»/
.Q_DolSuo * {quotes:'\201E' '\201D' '\2019' '\2018';}/„”’‘/
.Q_DolGdi * {quotes:'\201E' '\201D' '\BB' '\AB';}/„”»«/
.Q_GdiGsi * {quotes:'\BB' '\AB' '\203A' '\2039';}/»«›‹/
.Q_DulSul * {quotes:'\201D' '\201D' '\2019' '\2019';}/””’’/
.Q_Ja * {quotes:'\3010' '\3011' '\3016' '\3017';}/【】〖〗/
There is method in my class names. For example, DolGdo = Double opposite left Guillemot double outwards.
Hey Chris, you forgot to mention the
<cite>tag, which also relates to quotes.nope because the tag is no longer used for quotation (html4). In HTML5 it defines the title of a work.
@Aurélien
True, but in some countries, the quote marks are used for that, so the css may be set as “cite:before{content:open-quote;} cite:after{content:close-quote;}”.
@Gunnar Bittersmann
As I wrote before, associating quotes with a language may not be appropriate, as the quotes generally used online, and therefore what people will generally expect there, are mostly a variant of the ” … ‘ … ‘ … ” used in the US.
Now, one could just use those for a country, but their use is not consistent, and some authors may want to appeal to readers who DO expect to see the official country quotes, like the only one I found in France.
Hi,
in scss code, I am using “\201D”, however after grunt build its getting converted to “\201D”. I am not sure why. can any one help me out with this ?
Thanks
Prateek
Hi,
in scss code, I am using “\201D”, however after grunt build its getting converted to “\\201D”. I am not sure why. can any one help me out with this ?
Thanks
Prateek
If you are interested in seeing what online news sites are using for quotes in the countries you are interested in, go to: http://www.enewsreference.com/country_news.shtml
That page lists by country, each link going to a listing of all publications, each indicating if is online with ‘IN’, and in which languages it is available.
Re France, most online sites are in English, and of those in French, about half use US quotes. Times, they are a changing!
Very good, if you need german quote marks!
https://jsfiddle.net/bloggerschmidt/hnaw4p2j/
I don’t understand why the before and after pseudo-elements are required. When that whole block of code is removed, the single line of code (that includes the q selector and quotes property) seems to still work. What am I missing?!