The clear property is directly related to floats. If the element can fit horizontally in the space next to another element which is floated, it will. Unless you apply clear to that element in the same direction as the float. Then the element will move down below the floated element.
Here’s a simple example of a layout constructed with floats, which could be problematic for the footer:
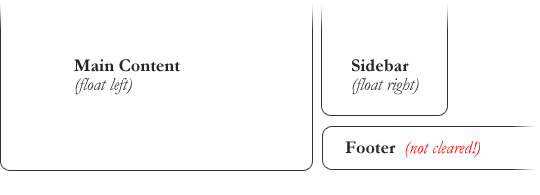
But by clearing the footer element, the layout snaps into place:
#footer {
clear: both;
}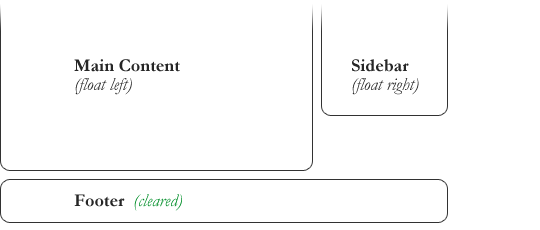
In this case, clear: both; was used to ensure the footer clears past elements that are floated in either direction. But you can also clear either left or right in which case the element will move below elements that are floated that direction, but not the other.
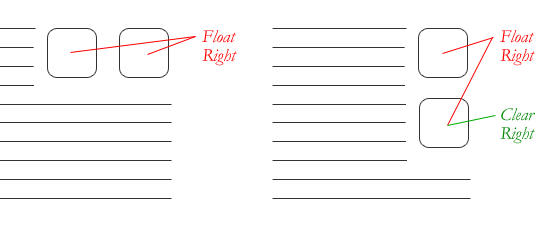
A common way to clear floats is to apply a pseudo-element to a container element which clears the float. Learn more about that here.
Other Resources
- All About Floats
- MDN
- Spec on the Visual Formatting Model (CSS2)
- W3C wiki on “Floats and Clearing” and a property reference.
- Noah Stokes: CSS Floats 101
Browser Support
The clear property works in all browsers.

Hello,
Could you provide code examples on clearing on the right or left only? The MDN examples don’t seem to have the kind of behaviour (move below elements that are floated that direction)…
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/clear
Thank you
https://css-tricks.com/all-about-floats/#article-header-id-2
That was helpful…